Frequently Asked Questions
Home & Building Automation
Electrical Services
Home & Building Automation
Home Automation
What is home automation?
Is home automation becoming a standard feature in properties?
Yes, particularly in high-end properties. The Samsung study shows that 25% of consumers consider smart technology a “must-have” in their next home, with 79% wanting a smart home as their next residence. Additionally, a report by Luxury Portfolio International states that smart home technology is now considered a standard feature in luxury real estate.
What are the main reasons to consider home automation?
Is home automation becoming a standard feature in properties?
How to choose the right home automation system?
When choosing a home automation system, it’s crucial to avoid closed protocol systems. These systems can limit your options to a single manufacturer, increasing the risk of obsolescence if the company goes out of business or stops supporting the technology.
To ensure longevity and flexibility, opt for open protocol systems like KNX. KNX is supported by numerous manufacturers worldwide, ensuring a wide range of compatible devices and ongoing support. Additionally, KNX’s compliance with international standards and its backward compatibility make it a future-proof choice, protecting your investment over time.
Do I need to rewire my property to install a home automation system?
Not necessarily. The need to rewire your home depends on the type of home automation system you choose and the existing infrastructure of your home.
- Wireless Solutions: Many modern home automation systems, including KNX, offer wireless options. These solutions can be installed without any major changes to your home’s wiring, making them ideal for retrofitting existing homes.
- Wired Systems: If you prefer a wired system for its stability and reliability, some rewiring might be necessary, especially in older homes. However, the extent of rewiring depends on the complexity and scope of the system you want to install.
- Hybrid Systems: Some systems use a combination of wired and wireless technologies, allowing you to enhance existing wiring with wireless components where necessary.
In summary, while a complete rewiring is often not required, a professional consultation can help determine the best approach for your specific needs and home setup.
Building Automation
What is a Building Automation System (BAS)?
The primary goals of a BAS are to enhance energy efficiency, improve occupant comfort, ensure safety, and streamline building operations. A BAS is essential for modern building management, providing a smarter, more efficient, and integrated approach to operating and maintaining facilities.
What savings can Building Automation System achieve in commercial buildings?
The installation of Building Automation Systems (BAS) in commercial buildings can achieve significant energy savings, typically ranging from 15% to 30%. The exact percentage can vary depending on factors such as the type of building, the extent of automation implemented, and the efficiency of the existing systems being upgraded. By optimizing HVAC, lighting, and other systems, BAS can reduce energy consumption, lower operational costs, and improve overall efficiency
What is the difference between a Building Automation System (BAS) and a Building Management System (BMS)?
While Building Automation Systems (BAS) and Building Management Systems (BMS) are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences between the two:
Scope and Functionality
- BAS. A BAS typically focuses on the automation of various building systems such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, and security. Its primary goal is to improve operational efficiency and occupant comfort through automated control.
- BMS. A BMS encompasses a broader range of functions, including the integration and management of BAS components. It provides comprehensive oversight of building operations, including energy management, maintenance schedules, and other administrative tasks.
Complexity and Scale
- BAS. Suitable for smaller to medium-sized buildings or specific areas within larger buildings where focused automation is needed.
- BMS. Ideal for larger and more complex buildings or campuses that require comprehensive management of multiple systems and extensive reporting and analytics capabilities.
In summary, while a BAS is focused on automating and controlling specific building systems, a BMS provides a broader and more integrated approach to managing all aspects of building operations, offering greater efficiency, insight, and control.
Can Building Automation System (BAS) be retrofitted to existing building?
Yes, retrofitting a building with a building automation system is absolutely possible. In fact, it’s a growing trend as building owners look to improve efficiency, comfort, and sustainability in existing structures. Here’s why retrofitting is a viable option:
- Technology advancements. Modern building automation systems, including wireless options like KNX RF, minimize disruption by using existing electrical wiring or wireless communication.
- Scalability. You can start with a core system like lighting control and expand later to include HVAC, security, and other features.
- Cost-effectiveness. Retrofitting is often cheaper than complete system replacement, especially when considering the potential energy savings and improved operational efficiency.
There are several factors to consider when deciding on a retrofit:
- Building size and type. Different systems are better suited for various sizes and purposes (residential vs. commercial)
- Existing infrastructure. Compatibility with existing wiring or the need for wireless solutions
- Desired functionalities. Identify the key areas you want to automate (lighting, HVAC, security etc.)
- Budget. Costs will vary depending on the chosen system and the complexity of the retrofit.
- Wireless systems. Like KNX RF, these avoid extensive rewiring, making them ideal for existing buildings.
- Open protocol systems. These allow for easier integration with existing equipment from different manufacturers.
Why choose an open protocol system like KNX?
Open protocols like KNX offer several advantages.
- Longevity. Unlike proprietary systems, KNX is supported by multiple manufacturers.
- Standardization. KNX is approved by international bodies like CENELEC, ISO/IEC, and ANSI/ASHRAE.
- Flexibility. KNX supports various communication media including Twisted Pair, Power Line, Radio Frequency, and Ethernet/WiFi.
- Future-proof. KNX ensures backward compatibility, allowing integration of older devices with newer ones.
- Budget. Open standard systems like KNX often offer a more cost-effective solution due to wider availability of components and potentially lower licensing fees.
- Technical expertise. KNX systems are generally easier for certified professionals to install and maintain compared to closed protocols requiring specialized knowledge.
About KNX
Introduction to KNX
The desire for comfort and flexibility in managing heating, lighting, and access control systems is on the rise, both in homes and office buildings. Simultaneously, there’s a growing emphasis on energy efficiency. People are seeking living and working spaces that are comfortable, sustainable, and secure – this is where automation comes into play.
However, achieving enhanced convenience and safety while reducing energy consumption requires sophisticated control and monitoring of all involved systems. This presents a significant challenge, as it typically necessitates extensive wiring from sensors and actuators to control centers. For professionals, this abundance of wiring translates to increased design and installation complexity, elevated fire risks, and escalating costs.
This is where KNX steps in as a solution. KNX technology offers a way to integrate and manage these systems efficiently, reducing wiring complexity and associated risks while still delivering the desired level of control and automation. By using KNX, professionals can create smarter, safer, and more energy-efficient spaces without the drawbacks of traditional extensive wiring systems.
Benefits of the KNX
- International Acceptance. KNX is recognized as an international standard (ISO/IEC 14543-3) and is also a European standard (EN 50090). It is widely adopted across many countries, making it a leading protocol for building automation worldwide.
- Wide Adoption: Over 500 manufacturers produce KNX-certified devices, ensuring a broad and diverse range of compatible products.
- Future proof technology. While others play catch-up with the Internet of Things, KNX is already a trusted standard. Choose KNX and stay ahead of the curve with future-proof technology at the heart of your automation solution.
- Flexibility and personalization. Mix and match devices from different brands to create your perfect smart home or building. KNX even plays well with other systems, giving you complete freedom to choose. It’s the one-stop shop for all your automation needs.
- A safe and secure system. In today’s world, security is a critical concern, and the demand for robust safety measures in control systems is growing rapidly. KNX, is dedicated to meet and exceed the most stringent security standards in the industry.
Areas of application for architects (video)
KNX for Interior Designers. Marrying Functionality with Aesthetics (video)
As an interior designer, you understand the importance of creating spaces that are not only functional but also visually appealing. KNX technology offers a perfect blend of advanced home automation capabilities and aesthetic flexibility, allowing you to seamlessly integrate smart home features without compromising your design vision.
KNX manufacturers recognize the importance of design in home interiors. They offer switches, panels, and control units in a wide array of unique designs. Whether you’re looking for sleek touchscreens, elegant glass panels, or traditionally styled switches, KNX has options to suit every aesthetic preference.
Electrical Services
Dometic installations
How long does it take to install an EV charger?
A typical EV charger installation takes about 2-4 hours, depending on the complexity of the installation and whether new wiring is required. We’ll provide a more accurate timeframe after assessing your property.
What is involved in installing an EV charger at home?
Installing an EV charger involves assessing your electrical system’s capacity, choosing a suitable location for the charger, installing the necessary wiring and circuit protection, and testing the charger to ensure it works correctly. Some EV chargers like ‘Tesla Wall Connector’ need installation of earth Rod or special EV Chargers Consumer Unit.
How often should electrical installations be inspected?
The UK Electrical Safety Standards recommend that homeowners have an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR) carried out every 10 years, or when moving into a new property. For rental properties, this is legally required every 5 years.
Why should I replace my consumer unit?
- To ensure your electrical installation complies with the latest safety standards and regulations. It can help prevent electrical hazards, improve the performance of your electrical system, and accommodate future electrical needs like solar PV, EV charging, or battery storage.
- Upgrading your consumer unit might be required during electrical work, if you have an outdated fuse box or consumer unit. All new or modified circuits must meet the latest BS 7671 Wiring Regulations for safety.
- If your existing consumer unit is visually damaged.
- C1 or C2 codes related to condition of Consumer Unit in EICR (Example. Busbar was damaged to fit circuit protective devices from different manufacturers)
Do I need an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR) before replacing my consumer unit?
It is strongly recommended to have an EICR prepared before replacing your consumer unit. If the customer refuses, a pre-work survey must be conducted to ensure there are no immediate dangers or conditions that could cause issues with the new installation
Are there any specific requirements for earthing and bonding when replacing a consumer unit?
Yes, the installer must verify that the main earthing terminal is connected to an adequate means of earthing, the main protective bonding is sufficient, the installation has adequate earthing arrangements for fault protection, the meter tails and distributor’s equipment have adequate current-carrying capacity, and the polarity of the incoming supply is correct .
What tests are performed after replacing a consumer unit?
After replacing a consumer unit, several tests are conducted, including checking the continuity of protective conductors, ring final circuit conductors, insulation resistance, supply polarity, fault loop impedance, and the functionality of RCDs. An Electrical Installation Certificate is then issued to the customer .
The safest way to do DIY electrics.
The safest way to do DIY electrics is NOT to do DIY electrics. Find a trusted trade person on www.niceic.com so you can stay safe.
Privately Rented Properties
What are the obligations of a landlord when ordering an Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR)?
Before the inspection and testing work begins, the landlord must ensure:
– The electrical installation is energized and an electrical supply is available. If the energy supply is via a pre-payment meter, this should be accounted for.
– Access is arranged to communal locations such as the intake position to the building, especially in the case of flats in blocks.
– Previous records like Electrical Installation
– Condition Reports (EICRs), Electrical Installation Certificates (EICs), and drawings are made available if in possession.
– Coordination with tenants to ensure pets are secured during the inspection and testing work
What should a landlord do if parts of the installation are inaccessible during inspection?
If parts of the installation are inaccessible, this should be stated as a limitation in the EICR. The landlord should ensure that all accessible parts of the installation within the agreed extent are made available for inspection. If inaccessibility is due to operational limitations, it must be justified and agreed upon with the inspector before starting the inspection.
What are EICR codes and how do they impact the outcome of an EICR?
EICR codes classify the condition of the electrical installation based on the level of danger or compliance. The primary codes are:
- C1 (Danger Present): Indicates an immediate danger that requires urgent action to make safe.
- C2 (Potentially Dangerous): Represents a potential danger that needs addressing but is not immediately dangerous.
- C3 (Improvement Recommended): Suggests that improvement is recommended to enhance safety, but it is not required for the installation to be considered satisfactory.
- FI (Further Investigation): Calls for further investigation to determine if a danger exists.
If any observations are classified as C1, C2, or FI, the electrical installation will be assessed as unsatisfactory for continued use. Remedial actions must be taken to address these issues. However, observations with a C3 code do not require immediate action for the installation to be deemed satisfactory but are recommended to improve safety and compliance
What is the importance of Portable Appliance Testing (PAT) for landlords?
Portable Appliance Testing (PAT) is essential for landlords to ensure the safety of electrical appliances provided to tenants. PAT helps identify any faults or potential hazards in the appliances, preventing electrical accidents. Landlords have a legal responsibility to maintain these appliances in a safe condition throughout the tenancy. Regular PAT ensures compliance with safety standards and reduces the risk of electric shock, fire, or other hazards associated with faulty electrical equipment
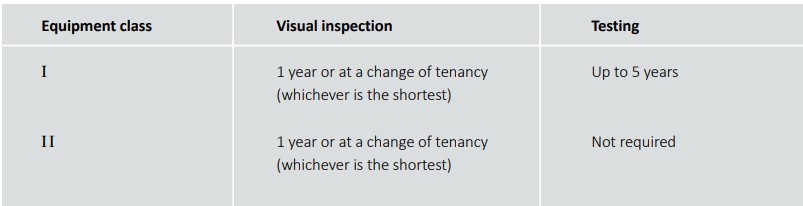
How often should PAT testing be conducted in rented properties?
The frequency of PAT testing in rented properties depends on the type and usage of the equipment. Generally, it is recommended that portable appliances be visually inspected every year or at the change of tenancy, whichever is shorter. Class I equipment should be tested up to every 5 years. New appliances should be inspected before use and added to the testing records. Second-hand appliances should be inspected and tested before being made available to tenants